SOFTWARE PRODUCTS
CANoe
CANoe is a comprehensive software tool supporting the entire development process from planning to system-level test for network designers, development and test engineers. It can develop, test and analyze individual ECUs and entire ECU networks in the automotive industries and various other such as aerospace, rail transportation and so on.
Multiple CANoe functions and configuration options are widely used by users around the globe. With its diverse application areas, it can provide accurate support to your project.
CANoe Advantage
- Complete all development and test tasks with only one tool
- Provide intelligent automated testing
- Simulate and test ECU diagnostics with a variety of options
- Evaluate results with clear text and graphics
- Notice and revise error situations in the early development stage
CANoe Application
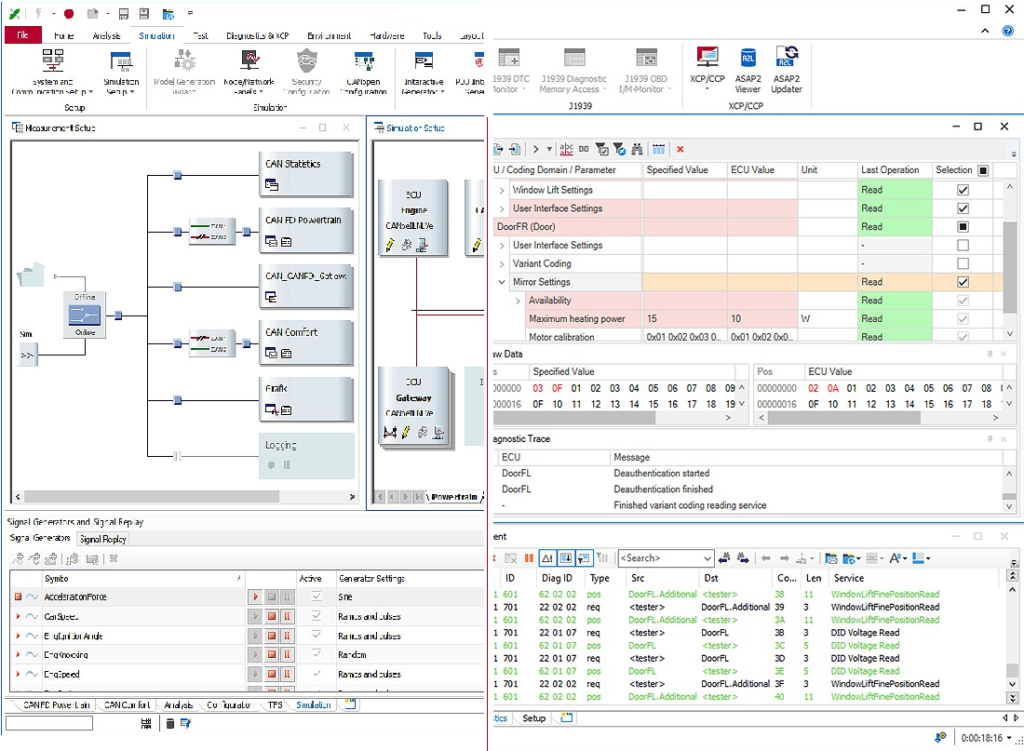
Diagnostics
There are various use cases for the diagnosis of ECUs, and they all can be combined with CANoe simulation of the ECU. During the process, interventions can be made at all essential communication layers. With CANoe DiVa, users can generate and execute diagnostic testing.
CANoe also supports all relevant automotive networks and transport protocols.
Types of diagnostic test include automated diagnostic test, semi-automated diagnostic test and interactive diagnostic test.
Automated diagnostic tests have several options such as CAPL or .NET test modules, test units and test case generation.
Semi-automated diagnostic tests help users record and play back repeated process.
In terms of interactive tests, diagnostic windows are available for all important use cases.
CANoe can record raw messages to show PDUs or even interpret the application/diagnostic level communication.
To ensure efficiency and flexbility in use cases in diagnostic area, CANoe has Diagnostic Channel and CAPL Callback Interface as solution.
Analysis
CANoe users can evaluate the information exchanged between ECUs and software functions. There are various CANoe analysis windows supporting user’s analysis work:
Trace Window: indicates all bus activities such as Error Frame and sending of messages. Individual signal may be displayed for each message even during measurement process.
Measurement Setup: Graphically represents and configures the data flow.
Scope Window: analyzes protocol errors and graphically depicts bus level measurement.
State Tracker: Indicates status information and displays digital inputs/outputs.
Video Window: records and plays back afterwards.
Map Window: Integrates GNSS information and maps.
Graphics Window: Graphically indicates the situation of signals (environment or values) with time.
Statistics Window: Shows bus activities with statistical data, including busload on node and frame level, counters/rates for frames and errors, controller states and burst counter/duration.
Data Window: Displays symbol values.
Write Window: displays system messages and outputs from CAPL programs of specific user.
Scene Window: Automatically draws ADAS objects according to their position and size after starting measurement.
Triggers and Filters: Reacts to specific bus events and reduces the amount of displayed or recorded data.
Testing
CANoe is the ideal testing tool for efficient ECU testing and the entire system. CANoe provides effective solutions on:
♦ ECU tests
♦ Module tests
♦ Integration tests
♦ Conformance tests
♦ Regression tests
♦ Testing of ECU prototypes
CANoe offers many open interfaces to adapt into testing environment:
♦ Integrating hardware for stimulation, measurement and injecting errors
♦ Interfacing MATLAB/Simulink models
♦ Controlling test systems via program calls, script calls
♦ Integration in higher-level test controllers
♦ Linking to external software tools
Simulation
Users can use the simulation function of CANoe to test and analyze a System Under Tests (SUT). SUT can be harware or software.
Components of a CANoe simulation include a real System Under Test (SUT) and one or more simulated remote stations. A SUT is not limited just to communication but can also interacts with its environment. Aside from the environment, environmental factors and physical effects can also influence the display of the simulation.
To create a CANoe simulation, all aspects of communication and the associated information of the individual simulation participants are required, and participants have to connect via communication channels so that data can be exchanged.
CANoe simulation has two variants. One is virtual SUT, which is operated only on a computer, and the other is real SUT, which is connected via a network interface. For real SUT, operating modes include interface mode, distributed mode and standalone mode.
Stimulation
During stimulation, events are applied to a System Under Test (SUT) to generate an expected response, and there are three main goals for the stimulus.
♦ The SUT is transferred to a desired target state and excitation are reproduced under control
♦ Several test scenarios are applied to SUT for analysis
♦ SUT responses are recorded to determine the ideal control parameters
The following methods help create a stimulation:
♦ Automation for command sequences (visual, Macro and .NET)
♦ Signal generators to create signal sequences with manual or periodic execution
♦ Signal replay for playing back a recorded signal course
♦ Various panels for manual stimulation and influencing of signals. The panels can be extended by the user if necessary
♦ Programmable processes in CAPL, .NET or C in the evaluation
CANoe Functions
Basic Functions
- Use of databases that describe the specific network (e.g. DBC, FIBEX, LDF, NCF, AUTOSAR System Description, MOST Function Catalog)
- Simulation of entire systems and remaining bus simulations
- Analysis of the bus communications
- Testing of entire networks and/or individual ECUs
- Diagnostic communication per KWP2000 and UDS and use as a fully functional diagnostic tester
- User programmability using the CAPL programming language to support simulation, analysis and testing
- Creating customized user interfaces to control the simulation and tests or to display analysis data
- Integration of additional I/O hardware and/or special test hardware (VT System)
- Intuitive user interface with flexible docking concept and user-friendly menu structures
- Support of new Vector bus hardware:
- For critical, realtime relevant simulations and tests, CANoe operates in a distributed mode on two PCs
- Numerous add-ons make it easy to adapt to OEM-specific services and protocols
- Diagnostic functions:
>Parameterization of diagnostics by diagnostic descriptions as ODX 2.0.1/2.2.0, MDX 2.0/3.0 or CDD
>Definition of simple diagnostic services with the Basic Diagnostic Editor
>Support of physical and functional addressing
>Quick and simple On-Board Diagnostics with built-in OBD-II tester
>Diagnostic observer for UDS and KWP2000 based on parameterizable diagnostic descriptions
>Transport protocol observer for ISO/DIS 15765-2
>Support of DoIP (Diagnostics over IP) and HSFZ (High-Speed Fahrzeugzugang)
>Special diagnostic CAPL functions for simulating and testing ECUs
- The Vector VT System enables comprehensive ECU tests in which I/O lines are used in addition to bus access
- Test cases may be linked to requirements using commonly used requirements tools such as IBM DOORS
- CANoe supports integration of MATLAB/Simulink models
- CANoe can be used as a runtime environment for the ECU code of AUTOSAR or OSEK-OS applications
- Access to internal ECU signals over XCP/CCP including protocol disassembly and analysis for CAN, CAN FD, FlexRay and Ethernet
- Control of digital and analog I/O modules as well as measurement hardware permits processing of real signal values in simulations and test environments
- Open software interfaces, such as Microsoft COM, FDX, FMI or ASAM XIL API, enable integration in existing system environments
- Access to connected systems with IoT protocols and backend with the Connectivity Feature Set (CFS)
Special Functions
More Options of Special Functionalities
Various kinds of software tools to facilitate the development process of automotive software.
Automotive
Higher Application Protocols
CANopen , ISO 11783 , J 1587 , J 1939 , SmartCharging
Measurement and Diagnostic Validation
AMD/XCP , DiVa , Scope , Sensor
Avionic System
A426, AFDX, CAN | A825